Eye diseases
Thyroid-associated orbitopathy
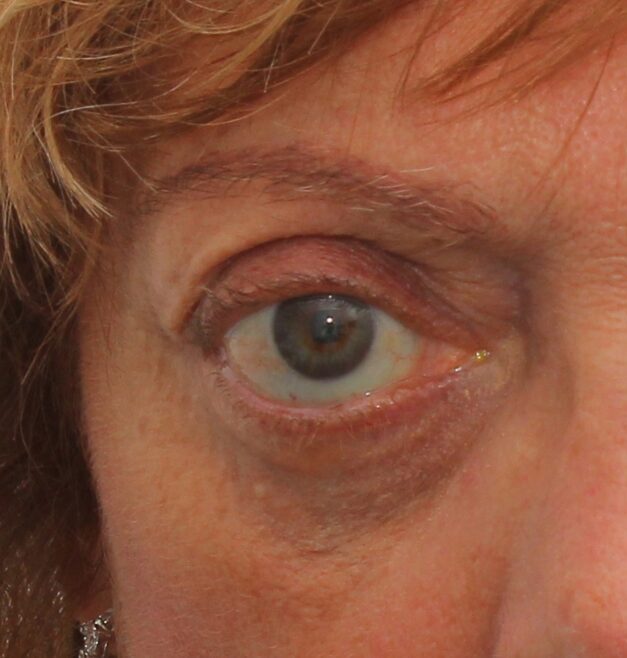
What is thyroid orbitopathy?
Thyroid orbitopathy is an eye disease of autoimmune origin, i.e. the body’s defences (antibodies) attack its own cells by mistakenly identifying them as invading agents. In this case, the antibodies are directed against the thyroid gland, making it more active than usual, which causes inflammation of the tissues of the eye orbit (eyelids, fat, extraocular muscles …) and the other soft tissues surrounding the eye.
We can differentiate between an active stage of the disease, in which the symptoms are more evident and severe due to the existence of a high inflammatory activity, and an inactive stage, in which the markers of thyroid orbitopathy may still be present, but not as virulently.
Symptoms
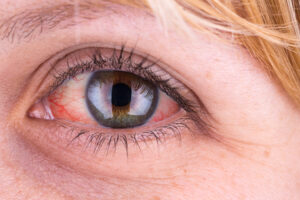
This disease is usually associated with “bulging eyes” or exophthalmos and alterations in the eyelids, such as eyelid retraction, as well as swelling and the appearance or increase of fat bags. Improper closing of the eyelids and increased exposure of the eye surface can cause eye discomfort and irritation.
If you have thyroid orbitopathy, it is also common for you to experience poor vision, when the cornea or the optic nerve is affected, as well as double vision due to the impact on the muscles responsible for eye movement and position. On the other hand, eye pain is a symptom that often occurs in the active stage of the disease as an effect of inflammation.