Eye diseases
Xanthelasmas
What are xanthelasmas?
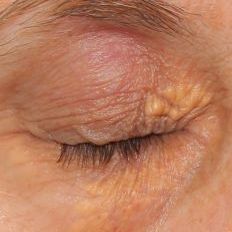
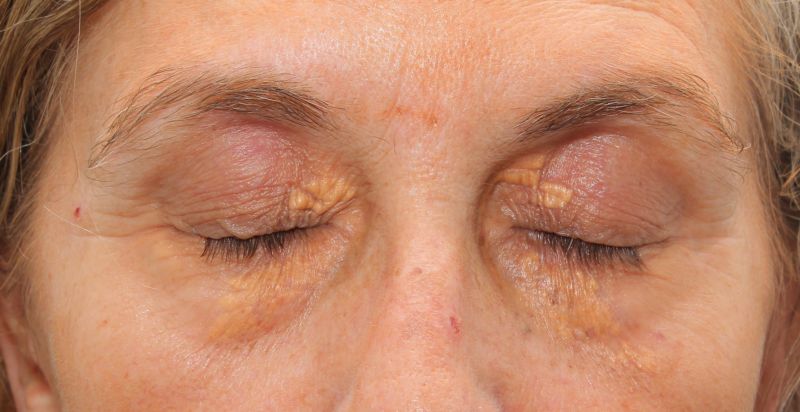
Xanthelasmas are small benign tumours, composed of cholesterol (fat) esters, which form under the skin of the eyelids or around them, often in the area near the tear duct.
We speak of unilateral xanthelasma, if these fatty accumulations are located in only one eye, and of bilateral xanthelasma, when it appears in both eyes. They can also appear in other body areas, such as the elbows, knees or buttocks (in which case they are called xanthomas).
Symptoms
Causes and risk factors
Treatment
Xanthelasmas are yellowish lumps that will feel more or less hard to the touch. They are not serious and generally do not cause any discomfort; they only represent an aesthetic alteration. However, they can obstruct vision if they grow and interfere with the field of vision.
You should also be aware that xanthelasmas do not decrease or disappear on their own.