Eye diseases
Blepharospasm
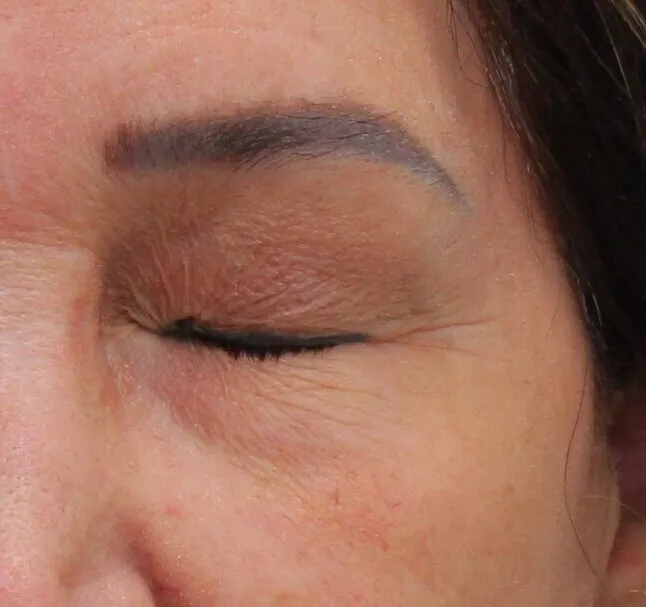
What is blepharospasm?
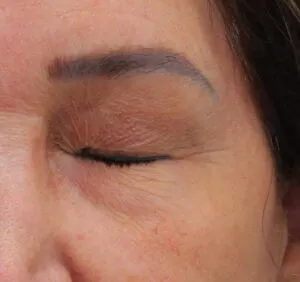
Blepharospasm is a disorder consisting of involuntary tonic contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle and the eyebrow muscle complex. This produces a complete and intense eyelid closure of varying duration.
It can have an ocular cause and, for example, be secondary to an injury, while being solved when the problem that causes it is cured. However, there is also a type of blepharospasm called “essential”, when we do not find a physical cause for it.
This pathology should not be confused with a twitch, another form of involuntary movement of the eyelids that is also due to a contraction of the orbicularis oculi muscle. However, while a twitch is a mild and temporary disorder, blepharospasm is chronic and can significantly impact quality of life.
Symptoms
Causes and risk factors
Treatment
Generally speaking, essential blepharospasm begins insidiously with an increase in blinking, while increasing its duration and intensity and eventually leading to photophobia, dry eye and inability to keep the eyes open.
It tends to get worse in the afternoon, due to stress and while you are listening or walking. On the contrary, it decreases when you talk, which makes it difficult to diagnose.
Sometimes it is accompanied by spasm in one area of the face (hemifacial spasm).